Blockchain and Applications, 4th International Congress
About this Book:
This book constitutes the refereed proceedings of the 4th International Congress on Blockchain and Applications 2022, BLOCKCHAIN’22, held in L’Aquila, Italy, in July 2022. Among the scientific community, blockchain and artificial intelligence are a promising combination that will transform the production and manufacturing industry, media, finance, insurance, e-government, etc. Nevertheless, there is no consensus with schemes or best practices that would specify how blockchain and artificial intelligence should be used together.
The 37 full papers presented in the main track were carefully reviewed and selected from more than 75 submissions. They contain the latest advances on blockchain and artificial intelligence and on their application domains, exploring innovative ideas, guidelines, theories, models, technologies, and tools and identifying critical issues and challenges that researchers and practitioners must deal with in the future research. The book also includes 3 papers from the WEB3-TRUST workshop and 2 papers from the Doctoral Consortium.
Referencia bibliográfica: Editors, Javier Prieto, Francisco Luis Benítez Martínez, Stefano Ferretti, David Arroyo Guardeño, Pedro Tomás Nevado-Batalla. Series Title: Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21229-1

Digital Content Verification Using Hyperledger BESU
Abstract:
One of the greatest current social challenges is the certification of digital content to guarantee its veracity and authenticity, and the possibilities offered by distributed ledger technologies thanks to the properties of the blockchain in terms of security, immutability, traceability and transparency provide a specific framework for this. This work presents the design of a prototype model within the Ethereum BESU network that can be scalable and interoperable with other DLTs. We have, therefore, studied both the regulatory and technological framework to design a tool that is capable of certifying digital content. In this work, we will only focus on the technological aspects according to the main certification modalities that exist today, and the main applications of blockchain technology for the management of certificates. We will conclude by explaining how the described prototype works as one of the central elements for the deployment of a platform specially designed in blockchain to detect fake news and fight against disinformation.
Referencia Bibliográfica: Alba, C.M., Benítez-Martínez, F.L., Ventura-Duque, M., Muñoz-Román, R. (2023). Digital Content Verification Using Hyperledger BESU. In: Prieto, J., Benítez Martínez, F.L., Ferretti, S., Arroyo Guardeño, D., Tomás Nevado-Batalla, P. (eds) Blockchain and Applications, 4th International Congress . BLOCKCHAIN 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 595. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21229-1_12
DOI: 110.1007/978-3-031-21229–1_12
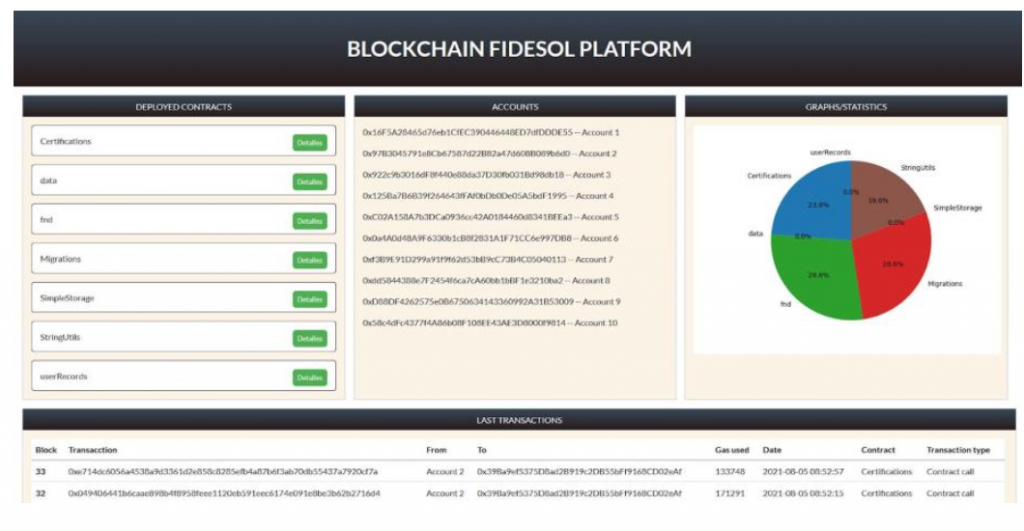

Neural blockchain technology for a new anticorruption token: towards a novel governance model
Abstract:
Blockchain technology currently represents a great opportunity for e-government in general and for public procurement in particular, given their financial implications and potential political and social risks. Blockchain technology facilitates the procedures and processes of administrative records via smart contracts because of properties such as timeproof sealing and data record immutability. In the present paper, we present a truthfulness governance approach which uses a permissioned model based on neural blockchain technology and smart contracts to create blocks within which all information is held in an on-chain consensus system to avoid corruption in the field of public procurement. Our proposal represents a scalable, efficient, innovative solution that is aligned with Sustainable Development Goal requirements and constitutes a ‘Decentralized Autonomous Organization’ in itself. Our model highlights the benefits of blockchain technology in terms of transparency, immutability, security, inclusiveness and disintermediation in order to create new anticorruption policies and technical solutions.
Referencia Bibliográfica: Francisco Luis Benítez-Martínez, Esteban Romero-Frías & María Visitación Hurtado-Torres (2022) Neural blockchain technology for a new anticorruption token: towards a novel governance model, Journal of Information Technology & Politics,
DOI: 10.1080/19331681.2022.2027317
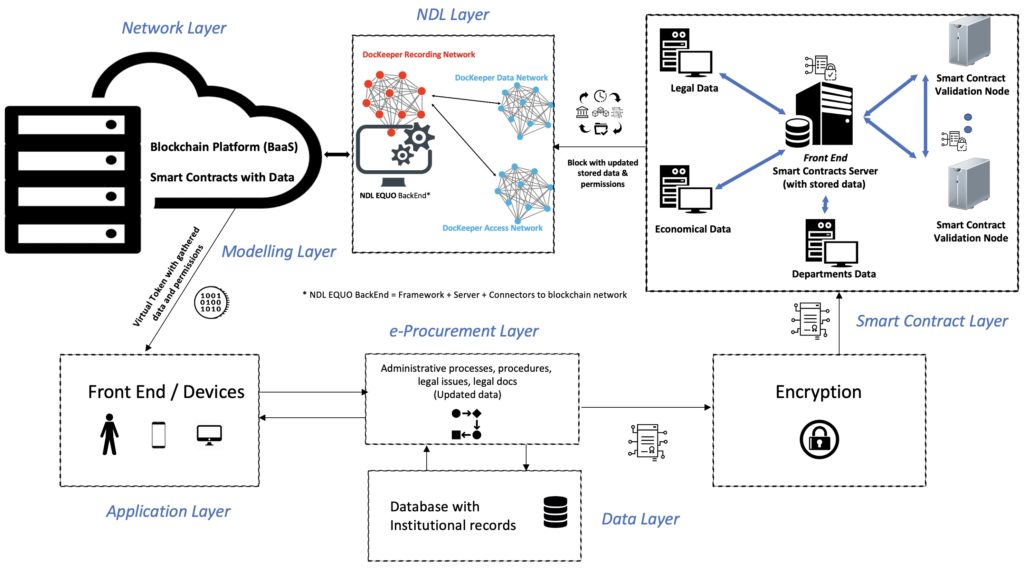

Blockchain as a Service: A Holistic Approach to Traceability in the Circular Economy
Abstract:
Today blockchain technology provides us with a formidable tool in the struggle to trace economic resources, especially in the context of the circular economy. The circular economy has been proposed as a key element in the transformation of production models in the context of European post–covid-19 recovery plans with particular reference to the Next Generation EU instrument. It is also a fundamental part of the European Green Deal. All of which comes under the umbrella of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals and the 2030 Agenda. The circular economy lays the foundations for the promotion of a new production and consumption model in which the value of products, materials, and resources remains within the economy for as long as possible, minimizing the generation of waste. This gives rise to a series of processes in which resource traceability is a key factor in preserving process integrity and guaranteeing process authenticity to the State, citizens, and companies. In this context, blockchain technology can provide solutions that are aligned with the 2030 Agenda. This technology facilitates the procedures and processes of logistics and of IoT sensor records via smart contracts through intrinsic properties that include timeproof sealing and data record immutability. In the present chapter, we describe the technological advantages that blockchain technology offers the circular economy. Sustainability is the cornerstone of blockchain models within the framework of the 2030 Agenda, so energy pollution in transactions or mining should be avoided. If we are able to overcome current environmental deterrents, distributed ledger technologies should represent a powerful tool in circular economy projects. In this chapter, we would hope to contribute to the debate on future paths towards sustainability. Specifically, we will describe how Blockchain as a Service-based traceability platform could be introduced into the circular economy while guaranteeing their straightforward but highly effective deployment in, for instance, the agrifood sector, at only minimal cost to SMEs. The underlying idea is based on finding blockchain solutions aligned with Sustainable Development Goals in order to ensure that the principal objectives and philosophy of the circular economy are upheld.
Referencia Bibliográfica: Benítez-Martínez, F.L.., Nuñez-Cacho Utrilla, P.V., Molina Moreno, V., Romero-Frías, E. (2022) Blockchain as a Service: A Holistic Approach to Traceability in the Circular Economy. In: Muthu S.S. (eds) Blockchain Technologies for Sustainability. Environmental Footprints and Eco-design of Products and Processes. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6301-7_6
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6301-7_6


Fundamentals of Blockchain and New Generations of Distributed Ledger Technologies. Circular Economy Case Uses in Spain
Abstract:
The evolution of Distributed Ledger Technologies since the first blockchain constitutes an opportunity for digital transformation in many social and economic contexts. This transformation will become even more intense in the post–covid-19 economic scenario. One of the most significant changes in the transformation consumers have undergone in their perception of the environment and of the sustainability of our societies. The circular economy is an agent of change that helps minimize humankind’s impact on the planet. And this change must be aligned with the sustainable development goals of the 2030 Agenda. Since its inception, blockchain technology has represented an opportunity for transparency, immutability, and persistence in the processes in which it intervenes, allowing it to be incorporated into easily traceable, disintermediated networks. By implication, this suggests we can move towards a verifiable, reliable, circular economy. In this chapter we cover the fundamentals of blockchain technology including its history, the elements that define distributed ledger technologies, and how they have evolved into their most recent forms—e.g., Hashgraph, Direct Acyclic Graphs, Holochain or Neural Distributed Ledgers—which represent scalable, efficient, innovative solutions aligned with sustainability goals and facilitating the efficient, sustainable management of circular economy projects. Finally, drawing on striking use cases in Spain, we describe the use of blockchain technology in circular economy projects, and its operating status, as examples of ideas for the future development of models that may reach the market.
Referencia bibliográfica: Romero-Frías, E., Benítez-Martínez, F.L., Nuñez-Cacho Utrilla, P.V., Molina Moreno, V. (2022) Fundamentals of Blockchain and New Generations of Distributed Ledger Technologies. Circular Economy Case Uses in Spain. In: Muthu S.S. (eds) Blockchain Technologies for Sustainability. Environmental Footprints and Eco-design of Products and Processes. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6301-7_2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6301-7_2
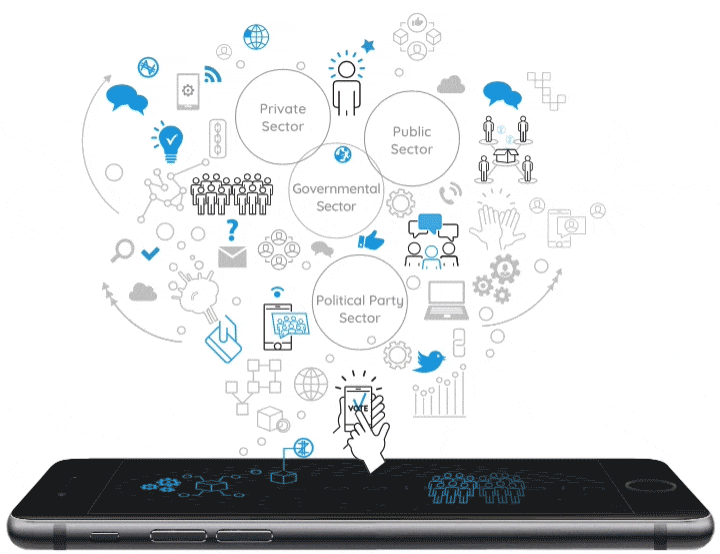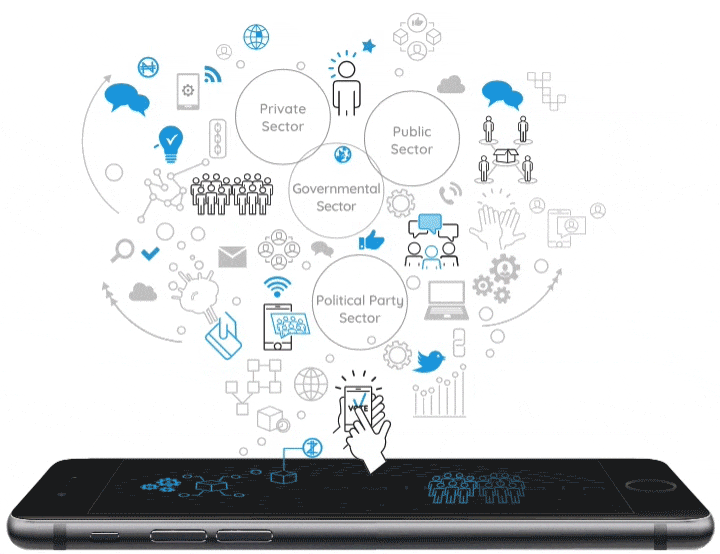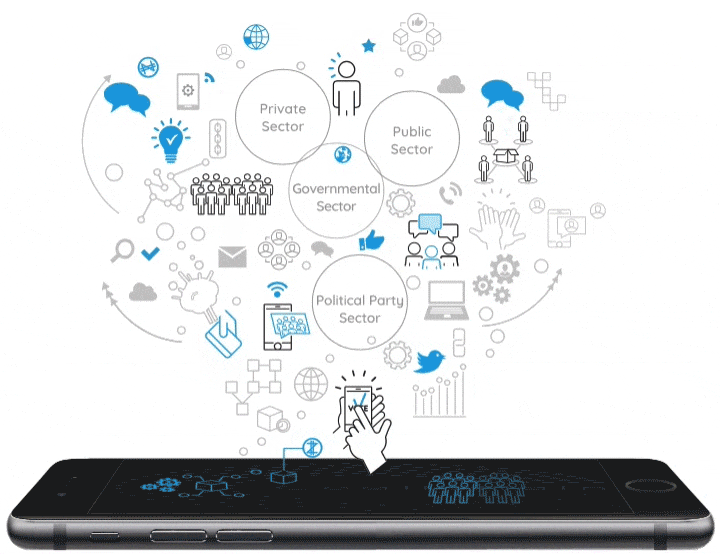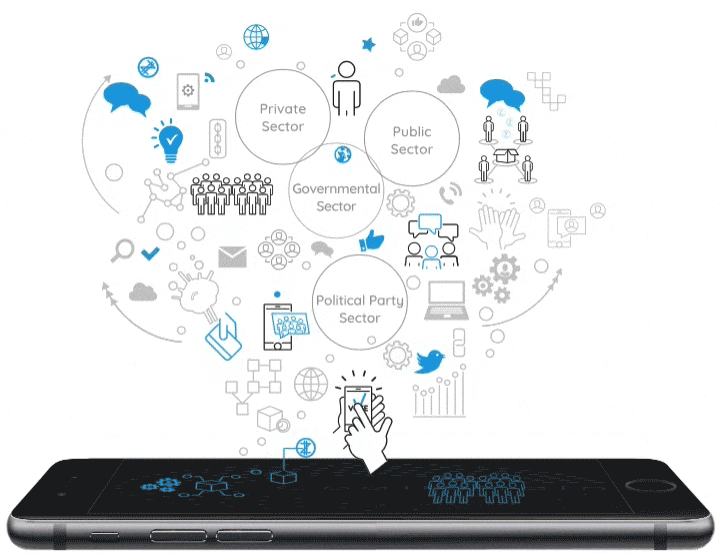
A neural blockchain for a tokenizable e-Participation model
Abstract:
Currently, Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs) and, especially, Blockchain technology represent a great opportunity for public institutions to improve citizen participation and foster democratic innovation. These technologies facilitate the simplification of processes and provide secure management of recorded data, guaranteeing the transmission and public transparency of information. Based on the combination of a Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) platform and G-Cloud solutions, our proposal consists of the design of an e-Participation model that uses a tokenizable system of the actions and processes undertaken by citizens in participatory processes providing incentives to promote greater participation in public affairs. In order to develop a sustainable, scalable and resilient e-Participation system, a new blockchain concept, which organizes the blocks as a neural system, is combined with the implementation of a virtual token to reward participants. Furthermore, this virtual token is deployed through a smart contract that the block itself produces, containing information about the transaction and all the documents involved in the process. Finally, our Neural Distributed Ledger (NDL) framework facilitates the interconnection of blockchain networks in a transparent, certified, secure, auditable, scalable and traceable way.
Referencia bibliográfica: Benítez-Martínez, F. L., Hurtado-Torres, M. V., & Romero-Frías, E. (2021). A neural blockchain for a tokenizable e-Participation model. Neurocomputing, 423, 703-712. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.03.116
Documento en pdf: https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/62228
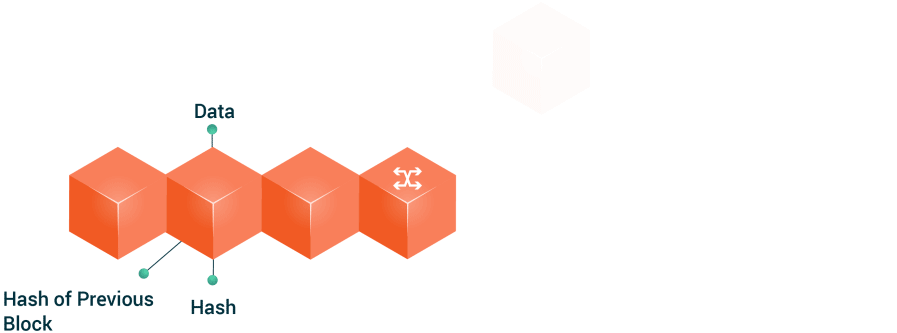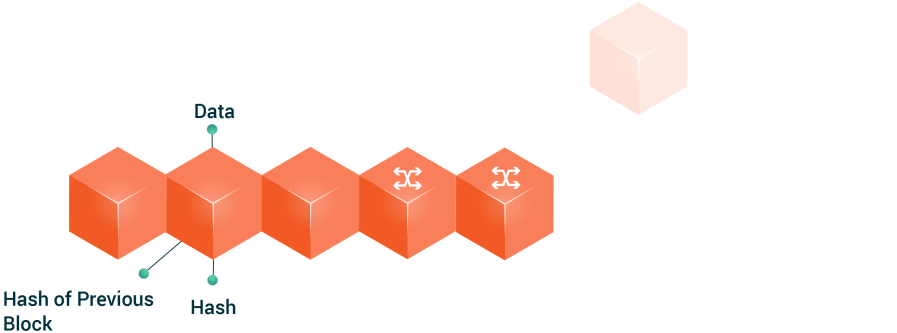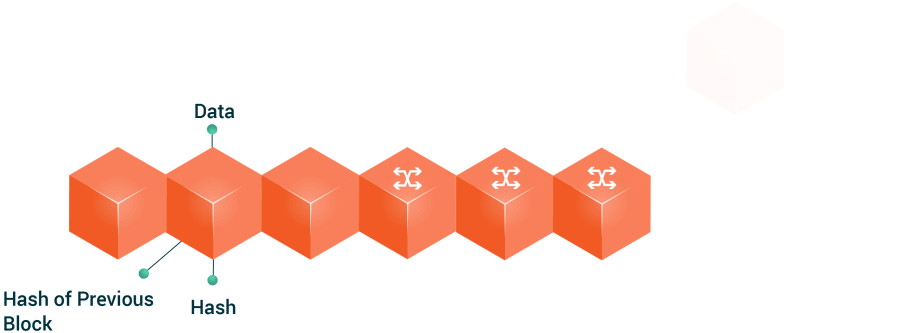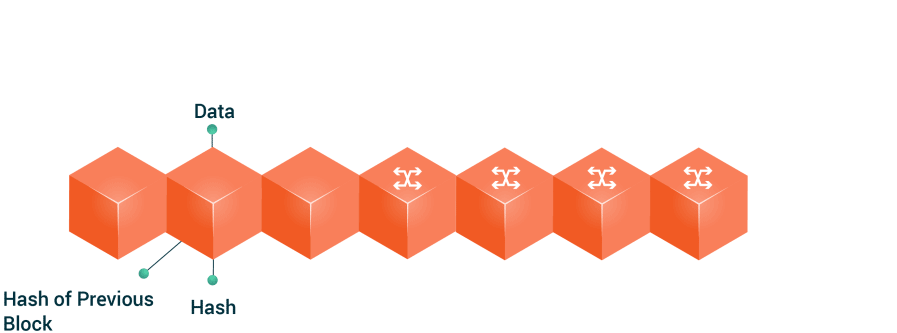

The “Tokenization” of the eParticipation in Public Governance: An Opportunity to Hack Democracy
Abstract:
Currently Distributed Ledger Technologies-DLTs, and especially the Blockchain technology, are an excellent opportunity for public institutions to transform the channels of citizen participation and reinvigorate democratic processes. These technologies permit the simplification of processes and make it possible to safely and securely manage the data stored in its records. This guarantees the transmission and public transparency of information, and thus leads to the development of a new citizen governance model by using technology such as a BaaS (Blockchain as a Service) platform. G-Cloud solutions would facilitate a faster deployment in the cities and provide scalability to foster the creation of Smart Citizens within the philosophy of Open Government. The development of an eParticipation model that can configure a tokenizable system of the actions and processes that citizens currently exercise in democratic environments is an opportunity to guarantee greater participation and thus manage more effective local democratic spaces. Therefore, a Blockchain solution in eDemocracy platforms is an exciting new opportunity to claim a new pattern of management amongst the agents that participate in the public sphere.
simplification of processes and make it possible to safely and securely manage the data stored in its records. This guarantees the transmission and public transparency of information, and thus leads to the development of a new citizen governance model by using technology such as a BaaS (Blockchain as a Service) platform. G-Cloud solutions would facilitate a faster deployment in the cities and provide scalability to foster the creation of Smart Citizens within the philosophy of Open Government. The development of an eParticipation model that can configure a tokenizable system of the actions and processes that citizens currently exercise in democratic environments is an opportunity to guarantee greater participation and thus manage more effective local democratic spaces. Therefore, a Blockchain solution in eDemocracy platforms is an exciting new opportunity to claim a new pattern of management amongst the agents that participate in the public sphere.

Tesis Doctoral: Un modelo de gobernabilidad para procesos de eDemocracia basados en una red neuronal de blockchain
Abstract:
Este trabajo de investigación está inspirado en la necesidad de establecer un nuevo marco tecnológico para espacios de democracia electrónica (eDemocracia), con el fin de desarrollar nuevos procesos de gobernabilidad y nuevas herramientas de empoderamiento ciudadano. Para ello utilizaremos el potencial de la tecnología blockchain para diseñar nuevos procesos y herramientas de eParticipación. La propuesta está orientada con una perspectiva bottom-up para ser impulsada desde las administraciones locales, como un modelo SaaS (Software as a System) apoyándose en la construcción de nubes públicas para facilitar su escalabilidad y despliegue. Se ha diseñado una herramienta específica, una dApp (aplicación distribuida) construida en un framework novedoso de blockchain, que está diseñado como una red neural distribuida, que facilita su ejecución e integración en los actuales modelos de gestión de la eAdministración. Se pretende construir un nuevo marco de gobernanza al servicio de la eDemocracia (una tecnogobernanza), para diseñar nuevos espacios de gobernabilidad ciudadana. La meta principal de este trabajo es la creación de una herramienta de eParticipación basada en una solución BaaS (Blockchain as a Service), llamada VoteKeeper diseñada como un modelo tokenizado de reputación y recompensas ciudadanos, por parte de la administración local, que permita una total transparencia de los procesos, garantice la privacidad de las opciones tomadas y permita nuevos espacios de empoderamiento ciudadano.
Referencia Bibliográfica: Benítez-Martínez, Francisco Luis. Un modelo de gobernabilidad para procesos de eDemocracia basados en una red neuronal de blockchain. Granada: Universidad de Granada, 2021. [http://hdl.handle.net/10481/65422]
Documento en pdf: https://digibug.ugr.es/handle/10481/65422